Optimize configuration for compute base on AWS Compute Optimizer
THEORY SECTION
what is AWS Compute Optimizer
AWS Compute Optimizer is a no additional charge for this service but should provide full permissions + metrics to analyze and make recommendations - help avoid over-provisioned or under-provisioned of the following 5 services:
- EC2 instances
- Auto Scaling groups
- EBS volumes
- Lambda functions
- Container service: ECS với máy ảo Fargate
Conclusion: within the framework of this lab, the cost optimization when using compute (EC2, Lambda, Fargate) should be done in the following order:
- Optimize instance type, configuration
- Once you are sure that instance type, configuration ensures the workload, proceed to purchase compute saving plans (refer to step 5 /en/5-ec2-updated-rec/)) to get discount up to 66% compared to on-demand payment
Note: if step 2 is complete before step 1, the optimization will be really meaningless, like how we are not sure if the machine is suitable for the workload work or not? too powerful - leading to redundancy, or too weak - resulting in not being able to handle the workload, which bought & committed to use that machine for 1 or 3 years .
What AWS Computer Optimizer relies on for analysis and recommendations
AWS Compute Optimizer relies on metrics collected by CloudWatch over a period of 14 days to analyze and make recommendations, with typical metrics such as:
- CPUutilization
- Memory utilization: mem_used_percent (Linux) or Available MBytes (Windows)
- VolumeReadBytes
- VolumeWriteBytes
In addition, the following metrics are available: link and custom metrics to be placed under a namespace is: CWAgent
Note: you can set a different namespace to easily track custom metrics in CloudWatch service, however if you want to get full recommendations from AWS Compute Optimizer then namespace: CWAgent is a required condition of this service.
Besides, the Memory utilization metric is custom metric so it is not initialized by default, the lack of this metric will make the choice of EC2 virtual machine configuration useless. misleading when recommendations are based solely on metric CPU utilization! Therefore, it is necessary to install CloudWatch Agent on EC2 virtual machines to collect metric memory.
Note: Refer back to step 1 to understand CloudWatch Agent link
Example 1: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for EC2 when only the CPU utilization metric is available.
- Current: EC2 has an instance type is m5.xlarge with 4 vCPU & 16 Gib Memory
- Option: there are 3 option to optimize instance type, option 1 is r6g.large with 2 vCPU & 16 Gib Memory
- CPU utilization: The above 3 recommendations are based on EC2’s CPU usage
- Memory utilizaton: there are no parameters for this metric, leading to the 3 options above are not really optimal
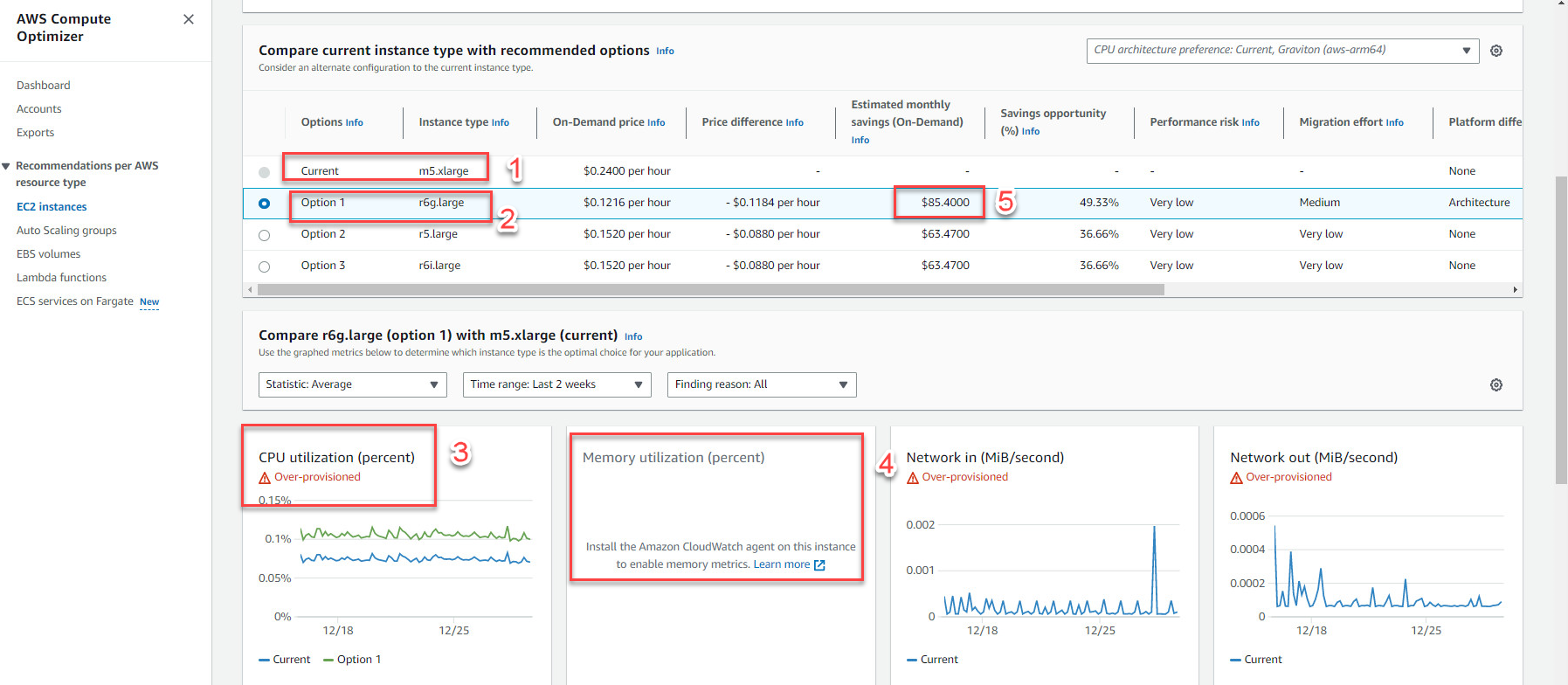
Note: monthly payment saved $85,4000
Example 2: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for EC2 when there are two important metrics: CPU utilization & Memory utilizaton
- Current: EC2 has an instance type of m5.xlarge with to 4 vCPU & 16 Gib Memory
- Option: there are 3 options to optimize instance type, option 1 is t4g.nano with 2 vCPU & 0.5 Gib Memory
- CPU utilization: The above 3 recommendations are based on EC2’s CPU usage
- Memory utilizaton: The above 3 recommendations are based on EC2’s Memory usage
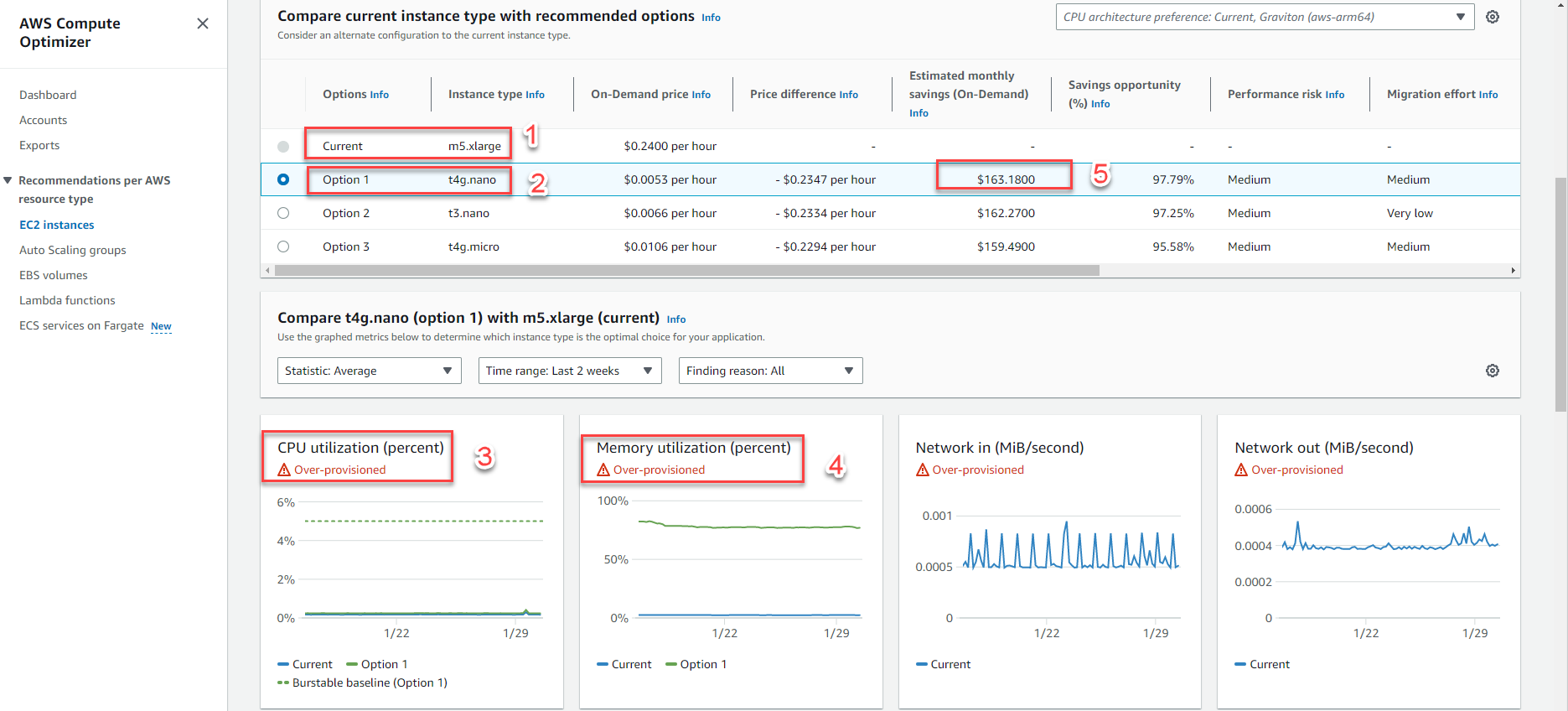
Note: monthly payment saved $163,1800 more than in example 1 -> From that, having full metric will help give the exact recommendation on actual usage, making savings most effective
AWS Compute Optimizer recommends for which instance types
AWS Compute Optimizer supports most instance types with common types such as: C5, M5, R5, T2, T3,… (reference)
AWS Compute Optimizer does not support the following instance types: G2, G3, G4ad, G4dn, G5, G5g, Mac1,…(reference)
Note: AWS Compute Optimizer is not recommended for Spot Instances
Conditions for AWS Compute Optimizer to recommend Auto Scaling group
- Run only one instance type (no multiple instance types)
- The values for the three assets: desired, minimum, and maximum capacity are the same (e.g. Auto Scaling group with fixed version number)
- No scaling policy attached.
- No overrides are configured.
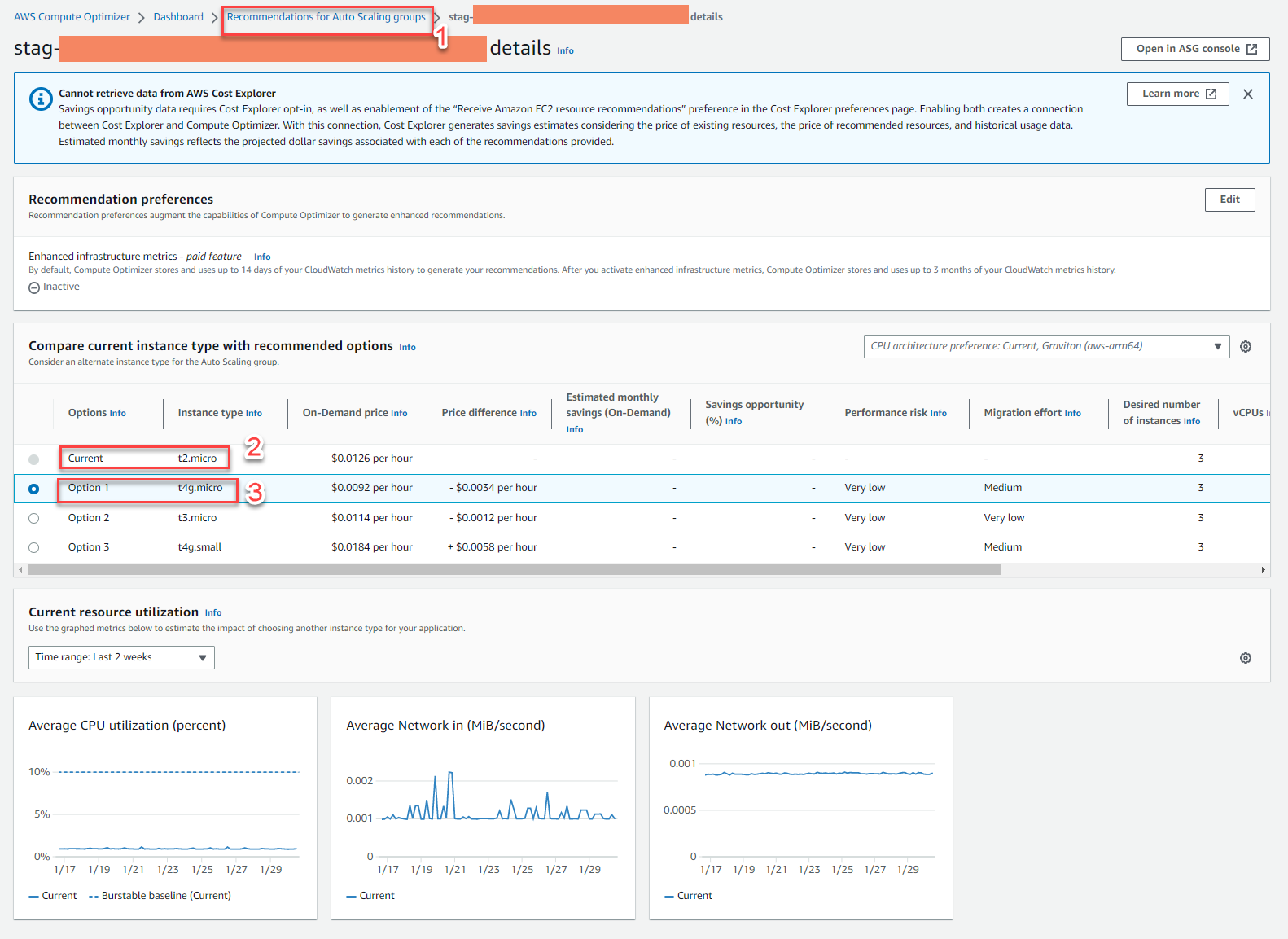
Example 3: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for Auto Scaling group = ASG, with ASG automatically generated when deploying the service AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Configuration details ASG
- Eligibility: Only run one instance type (eg: t2.micro)
- Satisfy the condition: the values for the 3 contents: desired, minimum, and maximum capacity are equal (eg: 3)
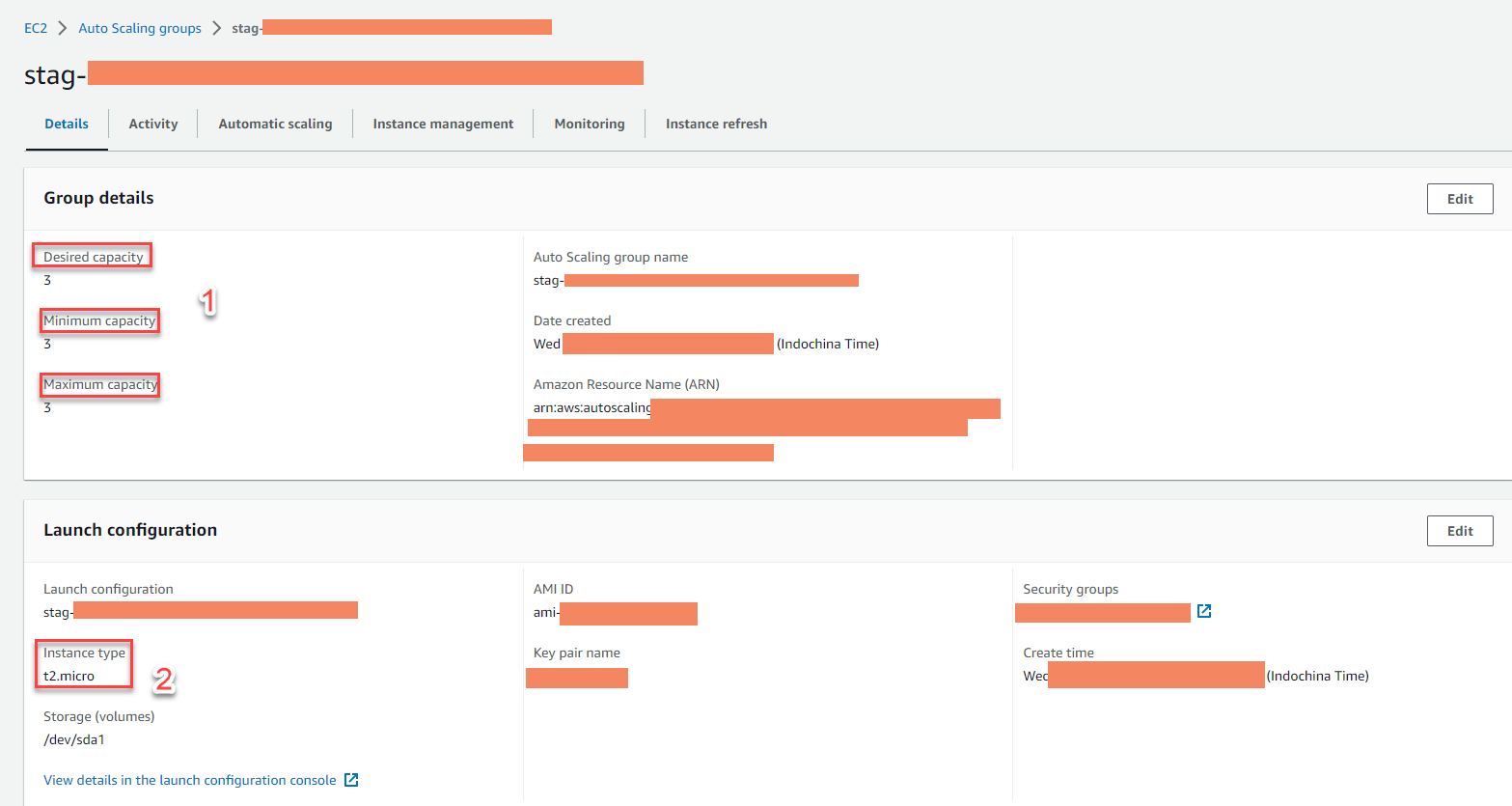
- Meet the condition without any scaling policy
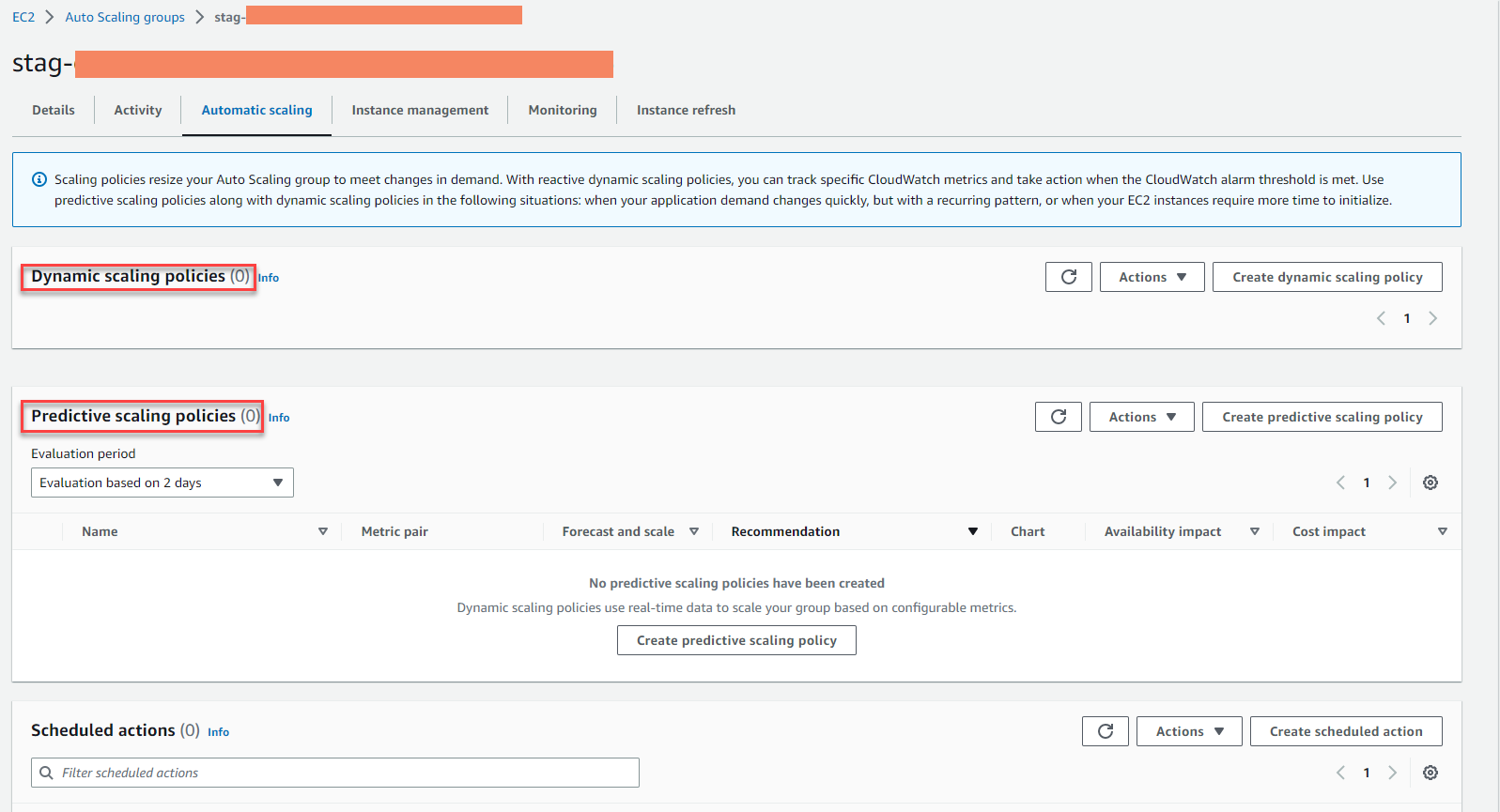
- Recommended service AWS Compute Optimizer
- Recommended for Auto Scaling group
- Current: ASG with current instance t2.micro
- Option: option 1 with to export t4g.micro for optimization, saving $0.0034 per EC2
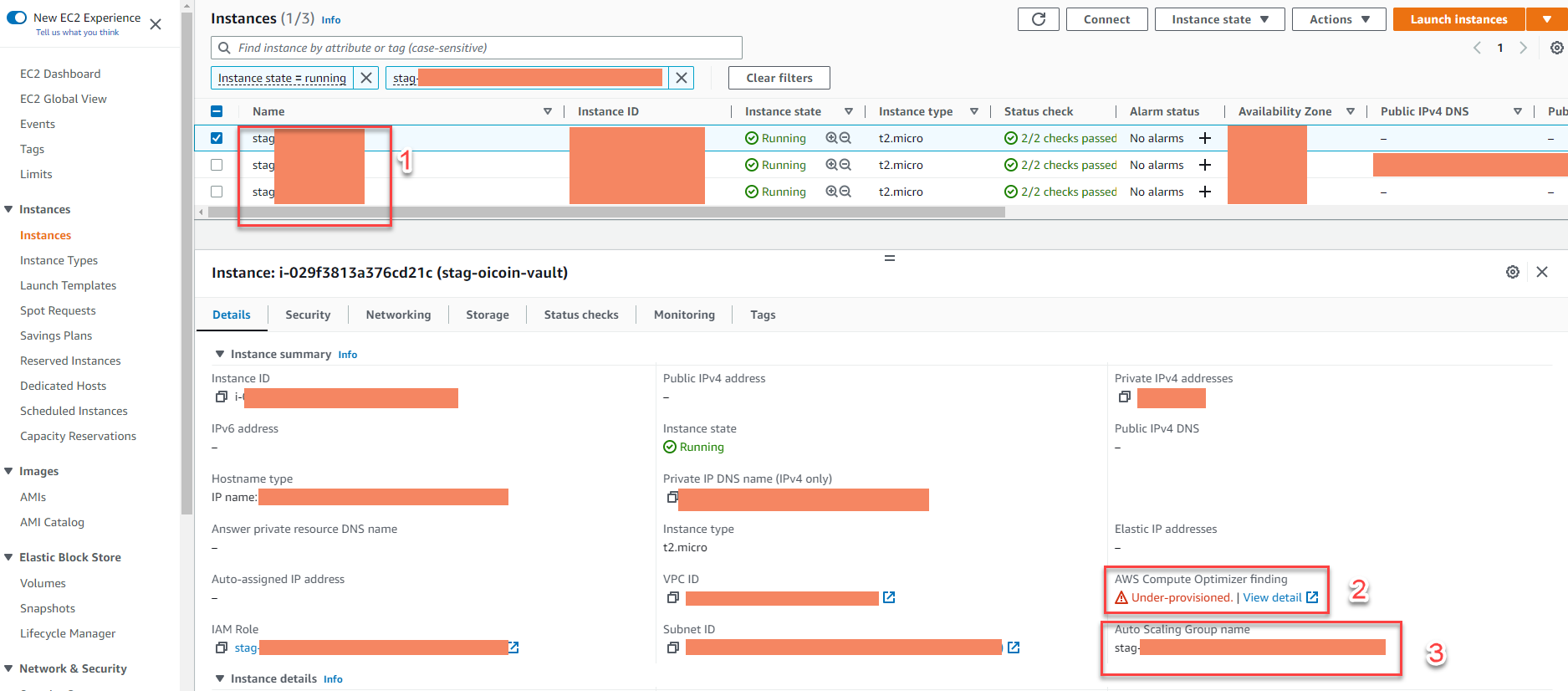
- Proposals are synchronized appearance on EC2 console
- Have 3 EC2 under ASG
- EC2s are in state: Under-provisioned
- These EC2s are being managed by ASG
Note: during use ASG with different demand between values eg: desired=2, minimum=1, and maximum=4 capacity, will not get optimization recommendations from AWS Compute Optimizer (learn more about Auto-Scaling-group service, link)
Conditions for AWS Compute Optimizer to offer EBS support
-
Recommended for EBS General Purpose SSDs (gp2 and gp3) and IOPS SSDs (io1 and io2) mounted in EC2.
-
EBS needs to be attached to an EC2 for at least 30 consecutive hours.
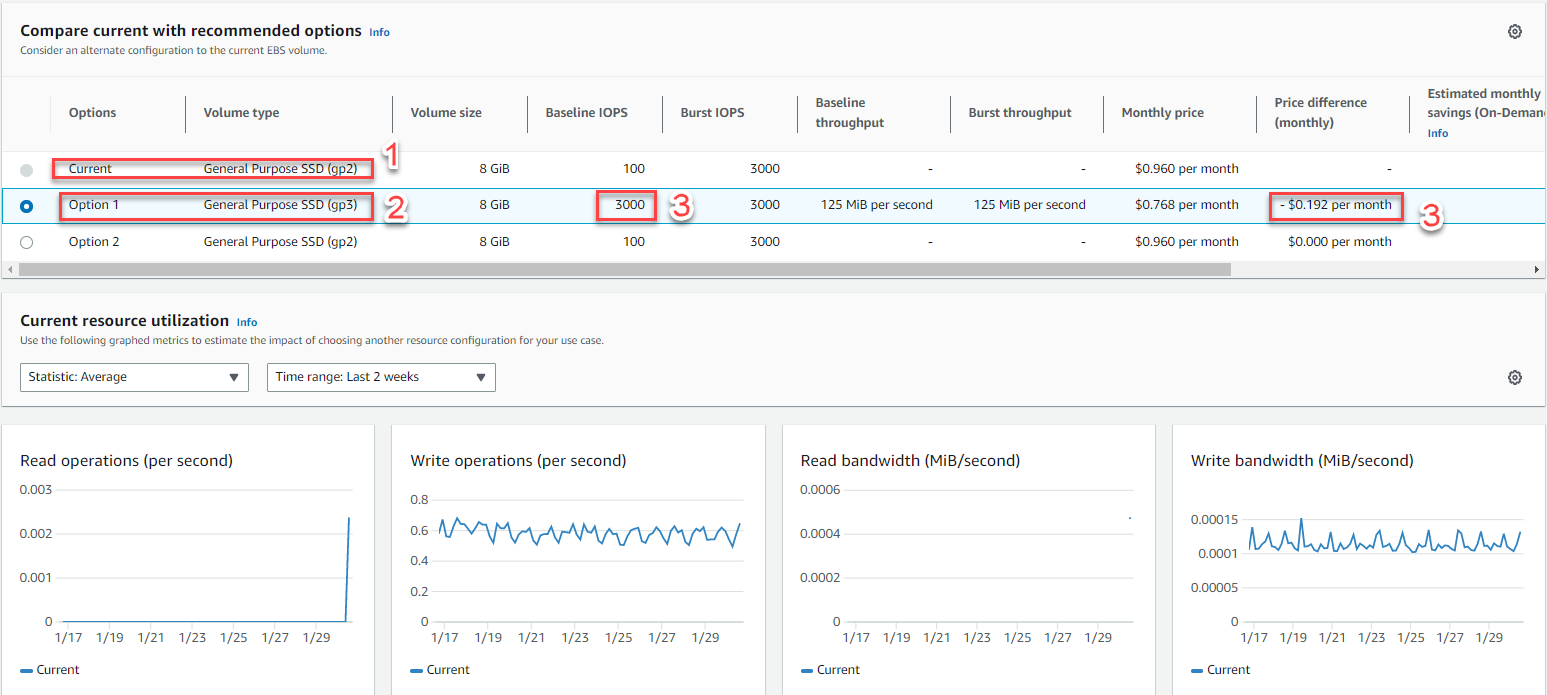
Example 4: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for EBS
- Current: SSD (gp2)
- Option: with option 1, it is suggested to use SSD (gp3)
- IOPS: increase to 3000 but cheaper, save $0.192 a month for 1 EBS drive
- In fact, the number of EBS drives is up to hundreds with Volume size of several hundred GB, the amount of savings is up to several hundred USD/month.
Conditions for AWS Compute Optimizer to recommend Lambda
-
Memory of lambda is less than or equal to 1792 MB (= 1.75 GB )
-
Lambda functions called at least 50 times in the last 14 days
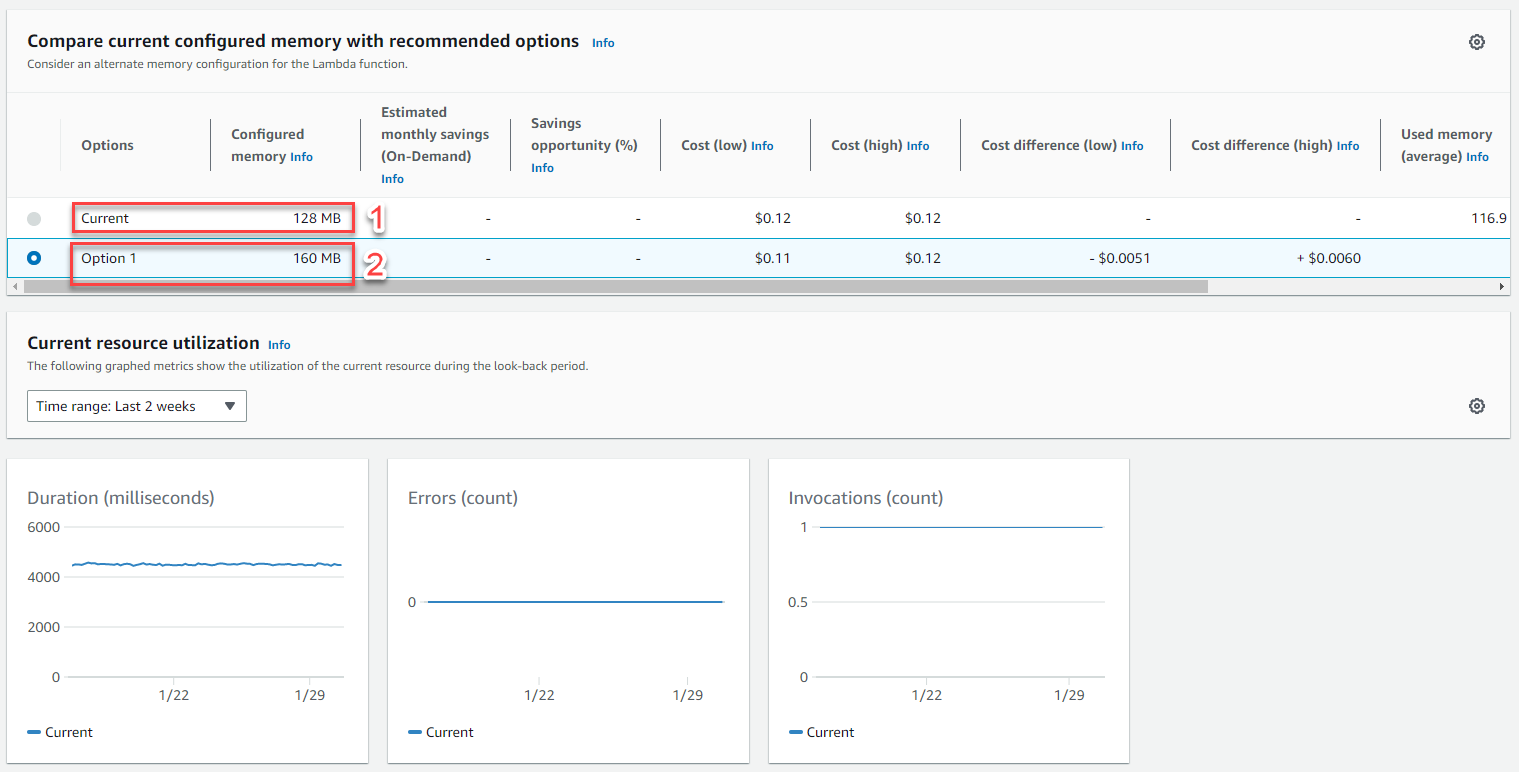
Example 5: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for Lambda
- Lambda is under-provisioned (Memory under-provisioned)
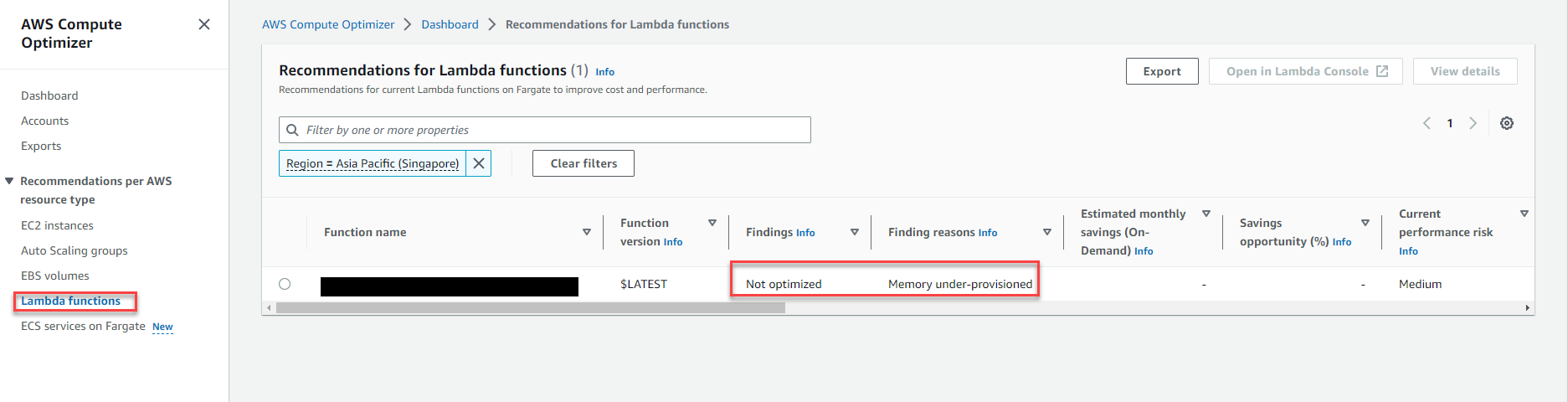
- Suggestion to increase memory for Lambda function
- Current: 128 MB memory
- Option: with option 1, it is suggested to use 160 MB memory
Conditions for AWS Compute Optimizer to offer Fargate support
-
Amazon ECS running on fargate with at least 24 hours of activity recorded by Cloudwatch
-
Have metrics of Amazon ECS utilization from the past 14 days
-
There are no step scaling policies assigned to Amazon ECS on fargate
-
There are no target scaling policies based on Amazon ECS CPU or Ram values on fargate
-
Fargate service has SteadyState or MoreWork status.
Note If target tracking policy is assigned to fargate service’s CPU, then AWS Compute Optimizer only makes recommendations for the size of memory and vice versa.
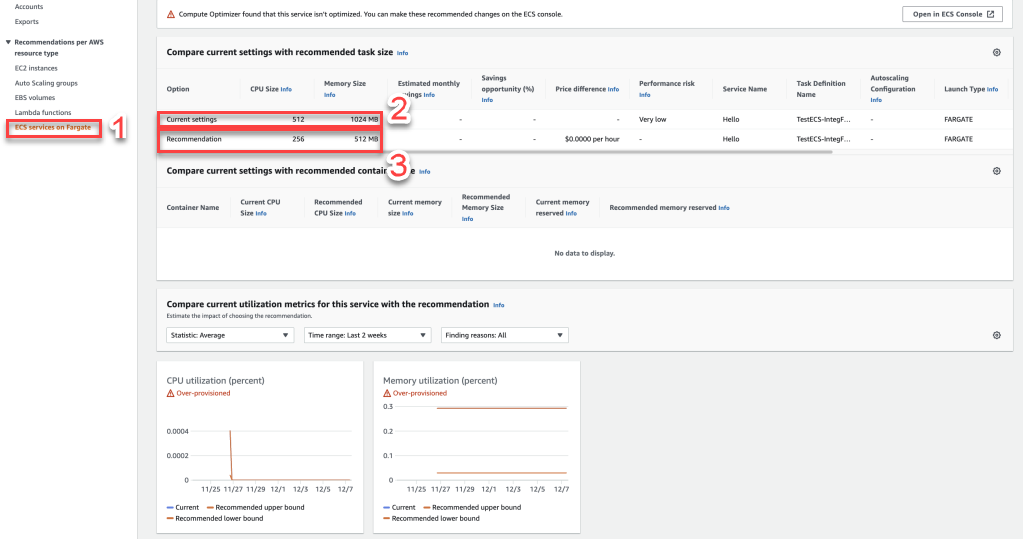
Example 6: The picture shows the AWS Compute Optimizer service proposal for Fargate
- ECS service on Fargate
- Current Setting: Current CPU and Memory
- Recommendation: for new CPU and Memory, more optimized and cost-effective when running in many compute.
IMPLEMENT SECTION
-
In this section, we will perform opt in AWS Compute Optimizer service! There won’t be any permision requirements if you are using IAM User with AdministratorAccess permision , but assuming you are 3rd and have plan to deploy the service for the production company, the customer only gives you least privilege to use the AWS Compute Optimizer service! So under the role of deployment you need to notify to your client about 2 policy below to get permission.
- ComputeOptimizerReadOnlyAccess (managed by AWS)
- Specific service-linked role for Compute Optimizer (managed by customer)
- Create policy service-linked role
- In the IAM console, select Policies
- Select Create policy
- Select JSON
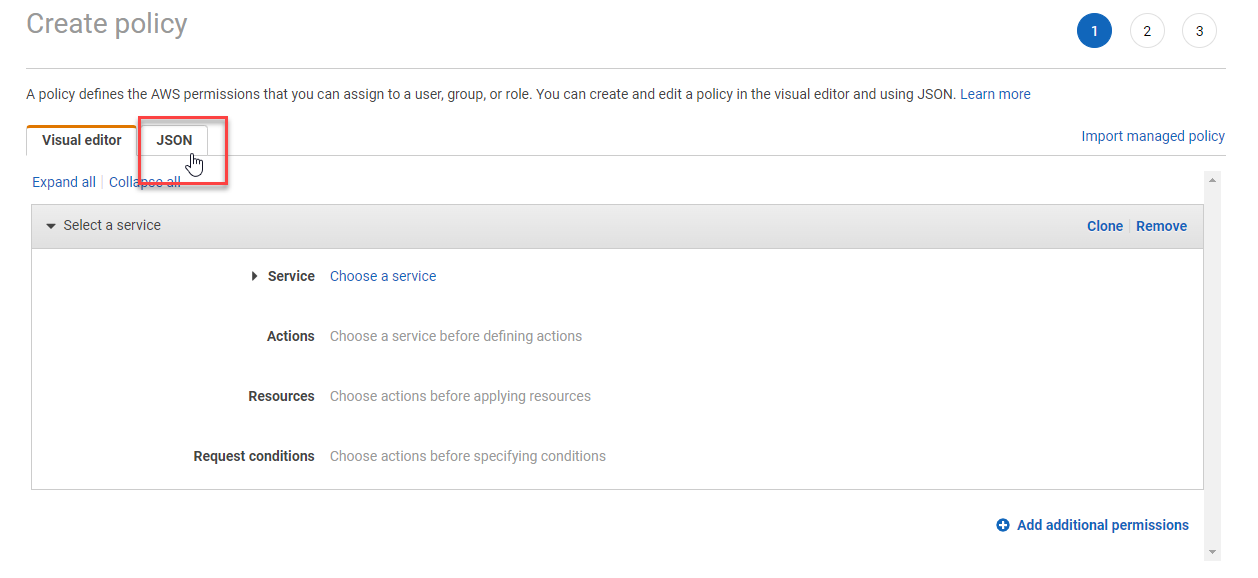
- Copy and pass the code below to box, chọn Next:Tags
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:CreateServiceLinkedRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/compute-optimizer.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForComputeOptimizer*",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"iam:AWSServiceName": "compute-optimizer.amazonaws.com"
}
}
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PutRolePolicy",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::*:role/aws-service-role/compute-optimizer.amazonaws.com/AWSServiceRoleForComputeOptimizer"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "compute-optimizer:UpdateEnrollmentStatus",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
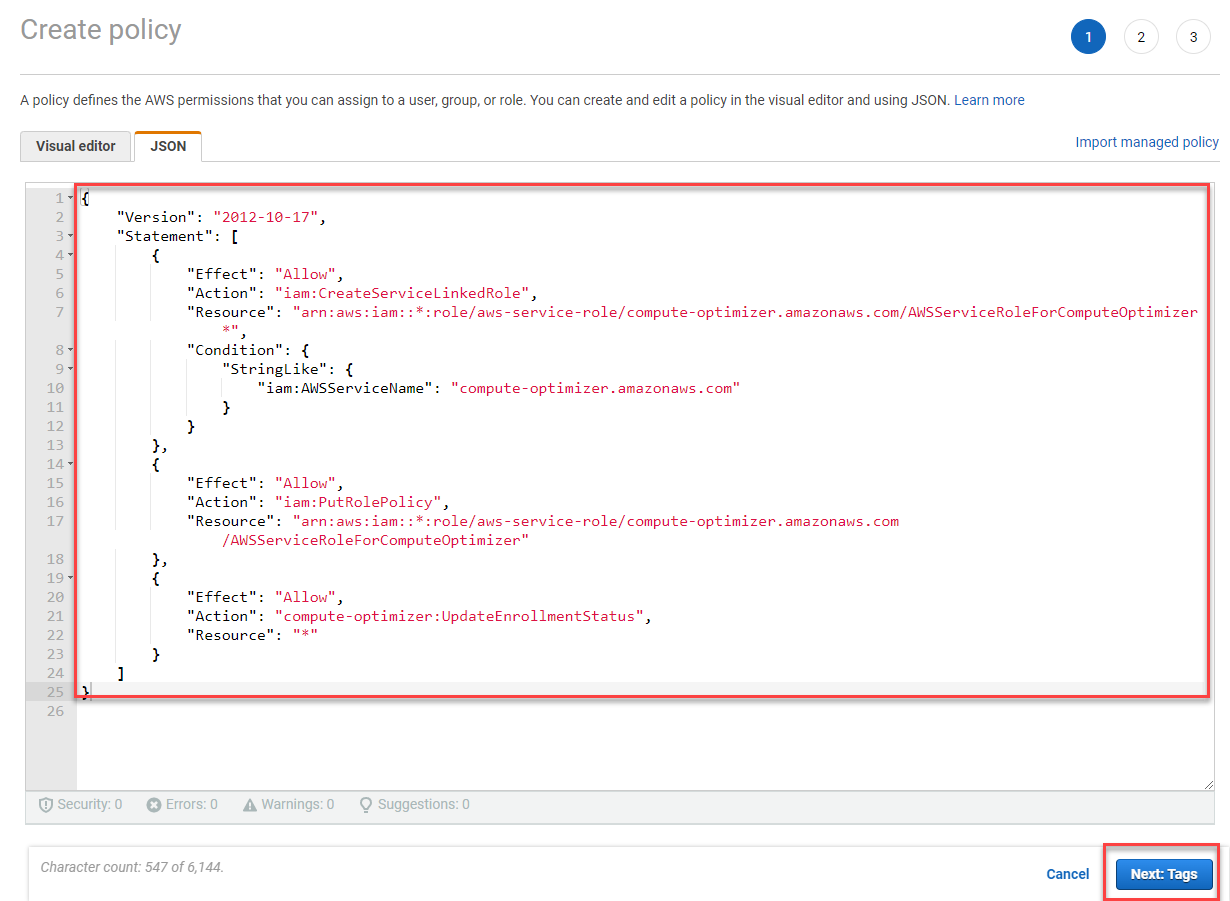
- Select Next: Review
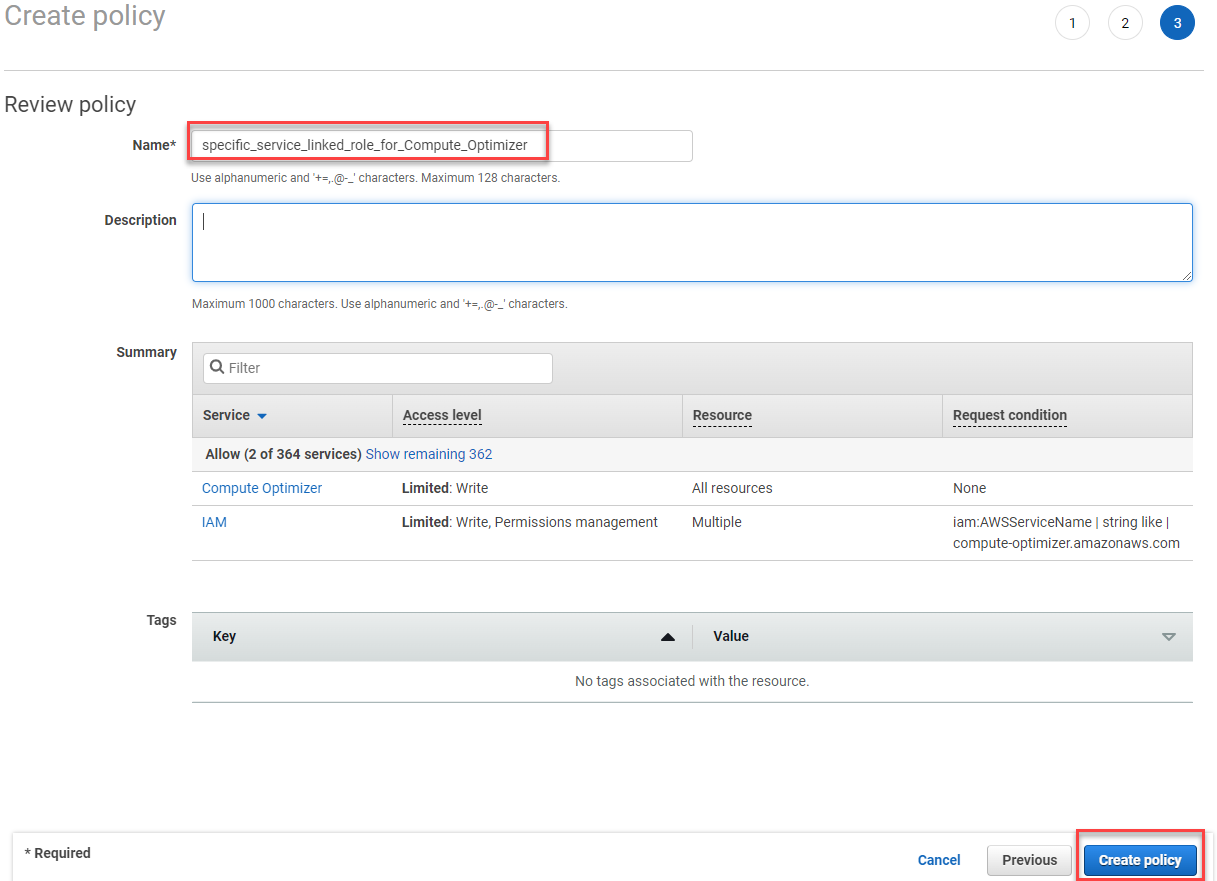
- In the page Review policy:
- Name:
specific_service_linked_role_for_Compute_Optimizer - Select: Create policy
- Name:
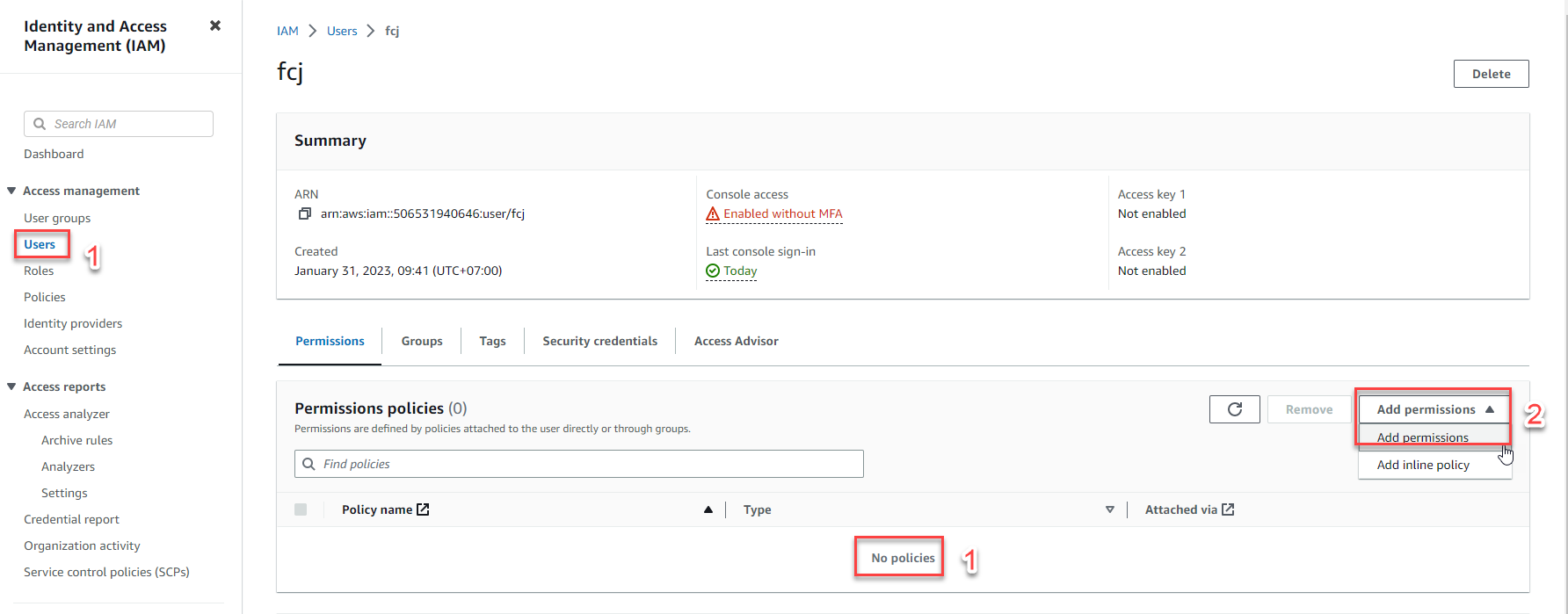
- Assign permissions to User
- Suppose you have a User but do not have any permissions policies as shown in the picture
- Select Add permissions
- Select Attach policies directly
- In the search box, type
compute - Select ComputeOptimizerReadOnlyAccess
- Select specific_service_linked_role_for_Compute_Optimizer (was created in the previous step)
- Select Next
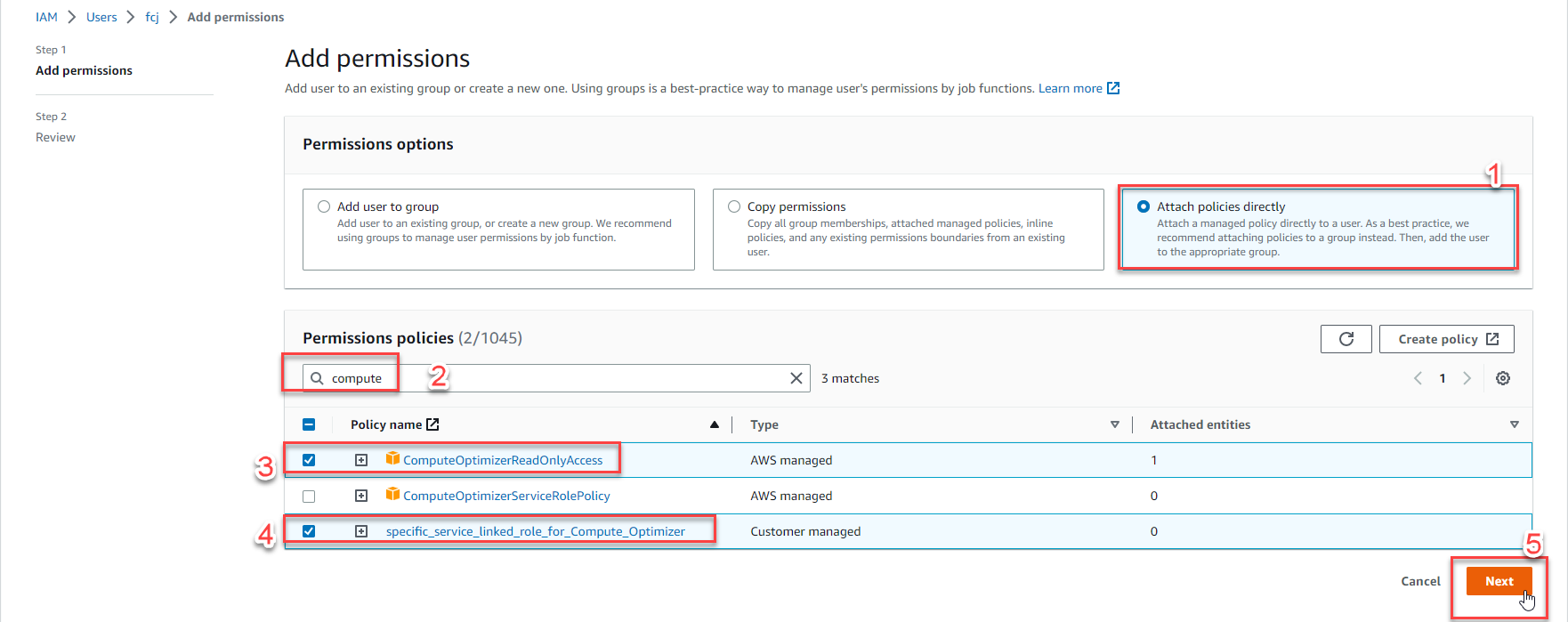
- Select Add permissions
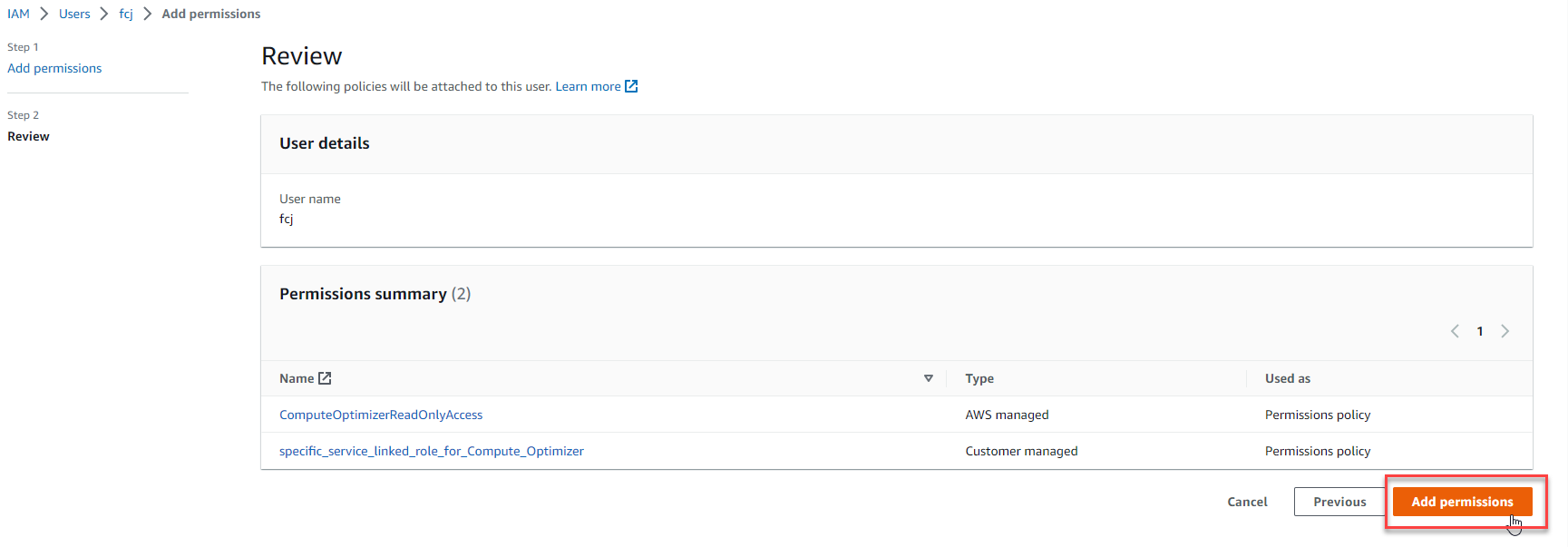
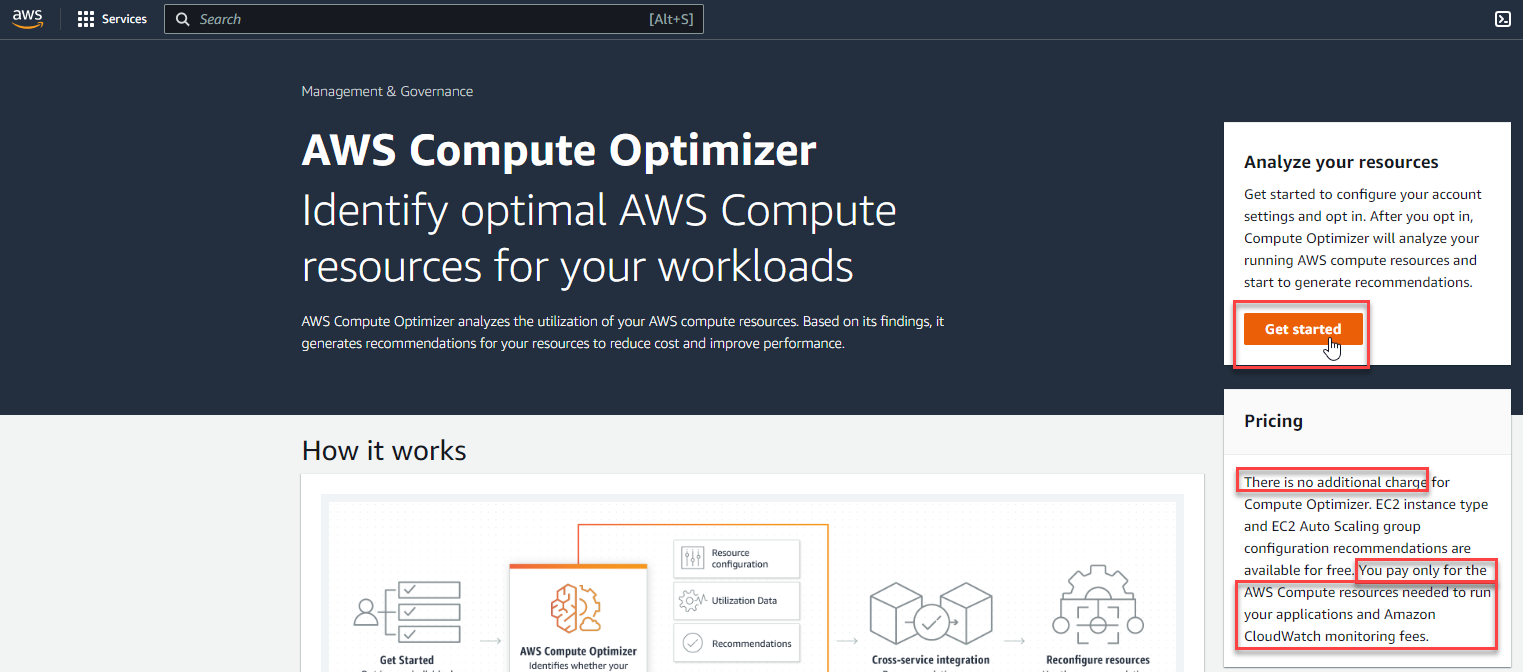
- Go on to Opt In AWS Compute Optimizer
- In the AWS Compute Optimizer console, select Get started
Note: AWS has a default notice, AWS Compute Optimizer service is free, we only pay when: change the configuration of compute + volumes and monitoring activities by Cloudwatch
- Select Only this account
- Select Opt in
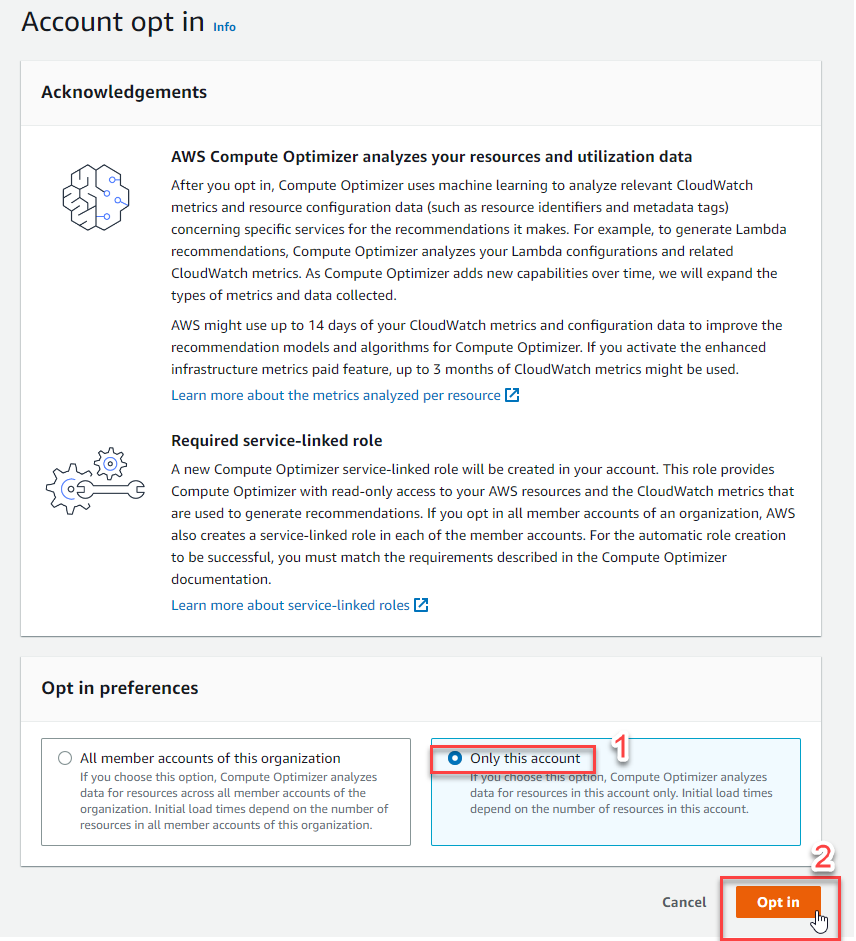
Note: In the framework of this lab, we will choose Only this account, but in the real business environment, when the customer splits 2 environments: Dev- Test and Production with 2 separate AWS accounts managed by AWS Organizations service (read more about AWS Organizations ). We will select All member accounts of this organization (located on the left) to get optimal recommendations for all compute and volumes included in the AWS accounts under organization
- In case, if you have not provided enough permissions for the User, the Opt in result will return information as shown below:
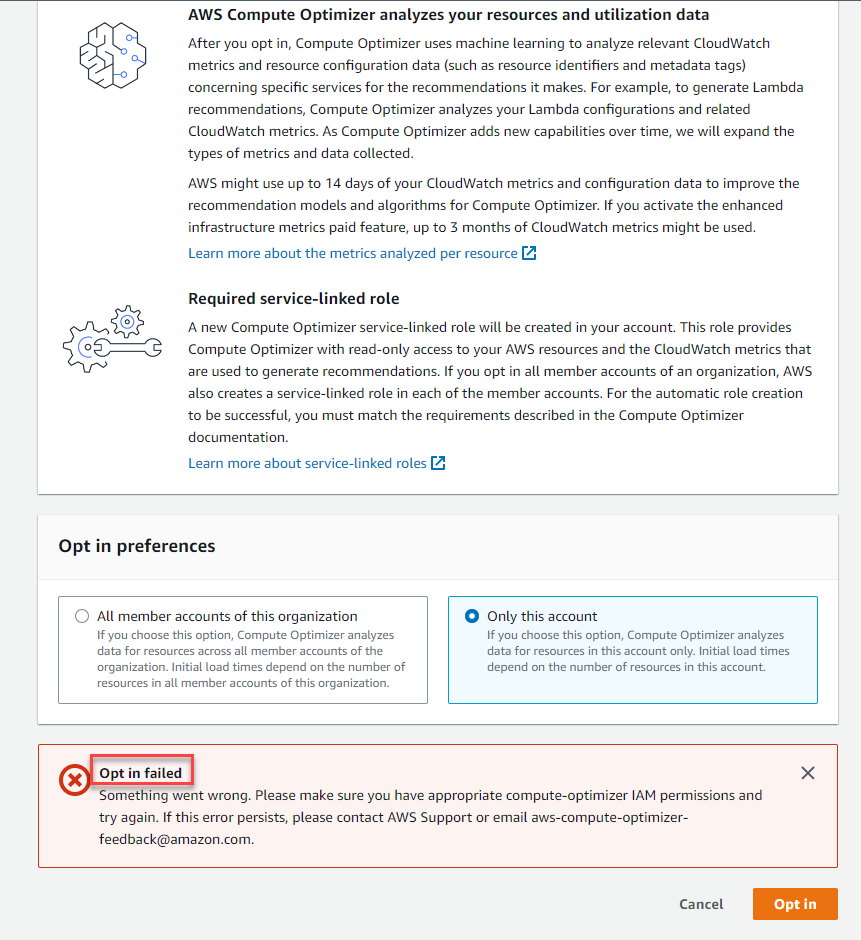
- Congratulations on your Opt in success, you won’t see any suggestions like the examples in theory for now as it can take up to 12 hours to complete AWS Compute Optimizer offers a recommendation.
- After 12 hours, with the resources that meet the conditions like theory above, you can click on the topics:
- Dashboard: for overview
- EC2 instances, Auto Scaling groups, EBS volumes, Lambda functions, ECS services on Fargate: review specific recommendations for resource optimization
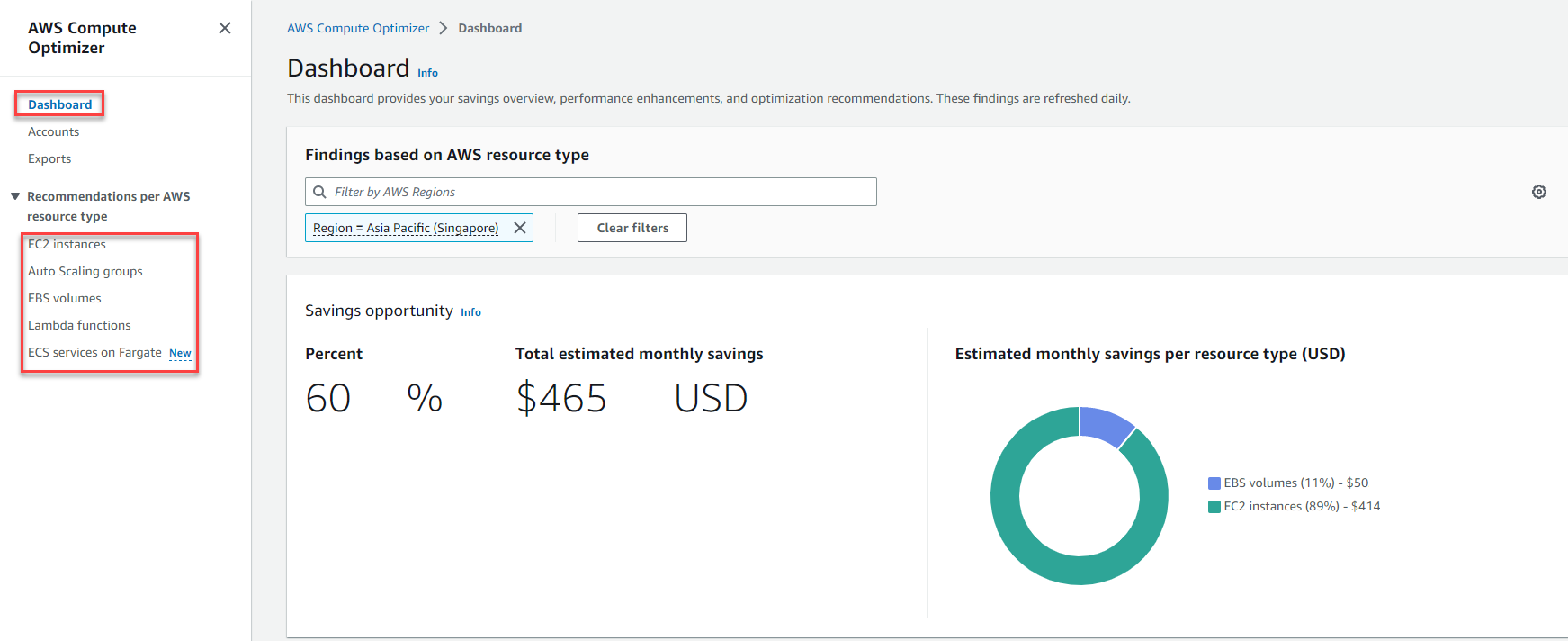
Note:
- For a full recommendation for EC2 based on the Memory + Ram metric, please re-read the above theory and refer back to step 1 to step 4 for better understanding and install CloudWatch Agent with namespace: as CWAgent (link)